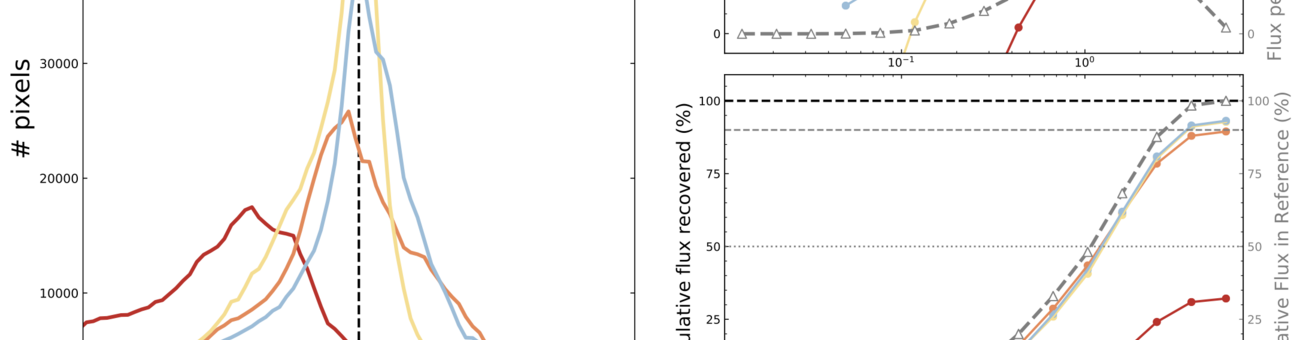
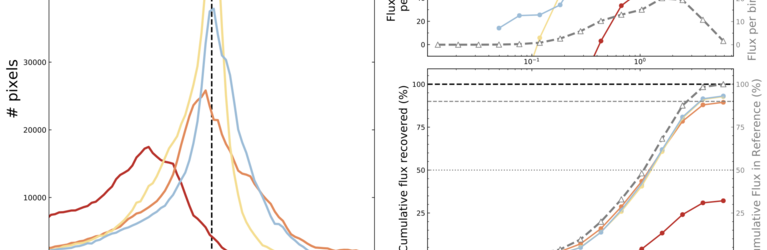
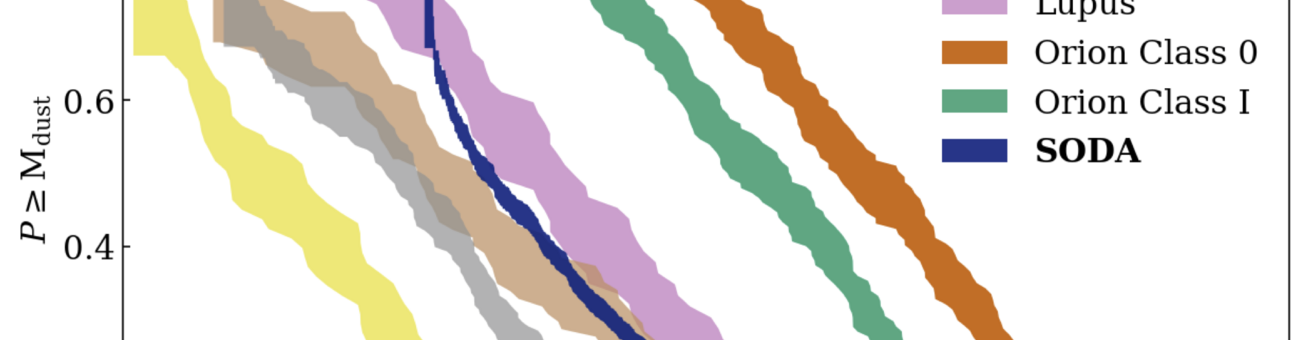
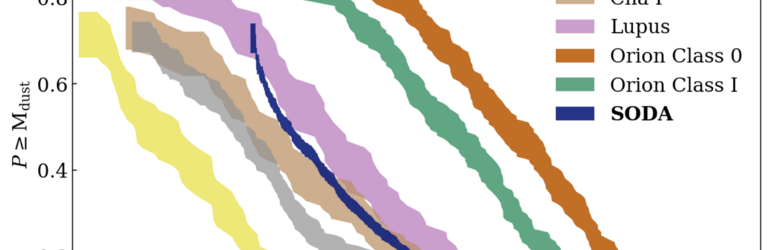
EMERGE ERC-StG: Emergence of high-mass stars in complex fiber systems
High-mass stars drive the physical and chemical evolution of the Universe. However, the origin of these massive objects is largely controversial. Three key questions remain under debate: a) Which physical processes determine the formation of high-mass stars? b) How do these stars get their large masses? c) Do high-mass stars form in a similar way to their low-mass counterparts?
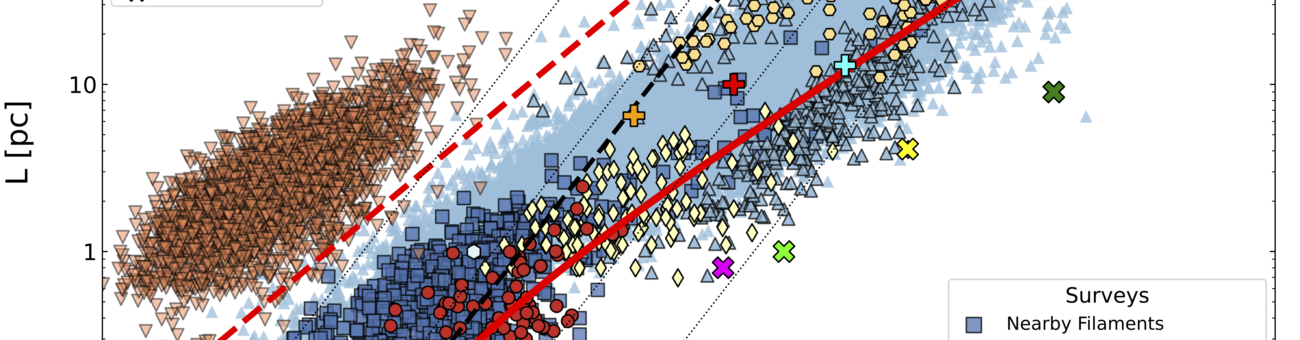
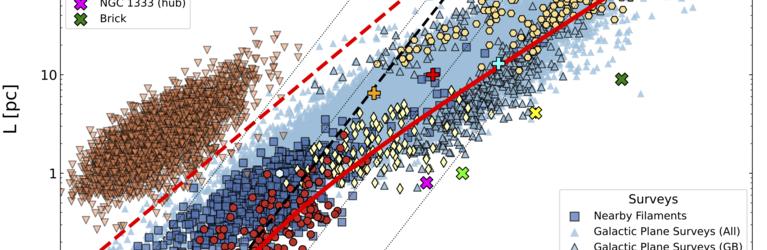
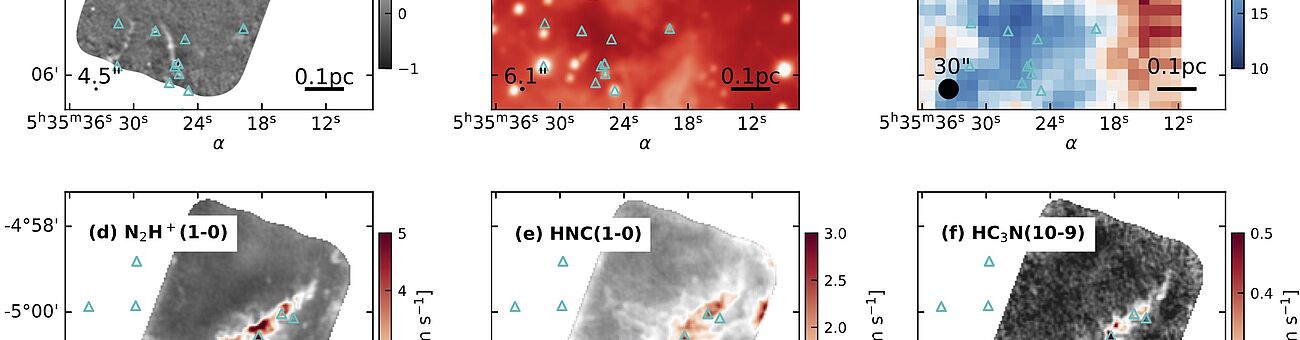
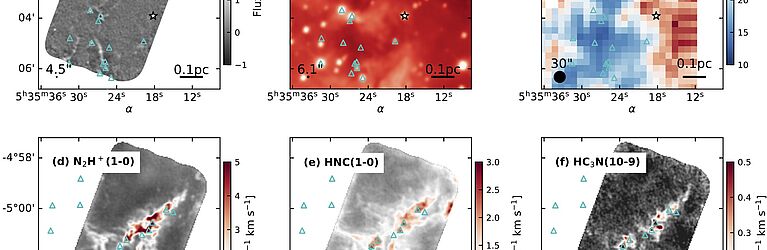
Galactic surveys link the origin of high-mass stars to the initial properties of their gas embryos. Using the Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA), Hacar et al (2018) recently proved the existence of a new and fundamental filamentary organization of the gas within the Orion Nebula, the nearest high-mass star-forming region. After leading this key discovery, EMERGE proposes to investigate the formation of high-mass stars as an emergent process in complex systems. In this novel scenario massive stars are created naturally by the internal interactions within networks of filaments of increasing density. To fully characterize this ground-breaking approach, this project will carry out the first systematic study of (1) the substructure, (2) internal interactions, and (3) dynamical evolution of these filamentary systems across the Milky Way.
EMERGE will survey a homogeneous ALMA sample of massive filamentary networks, the largest of its kind, extracted from the first intensive exploitation of its public archive. These observational results will be tested against state-of-the-art simulations using a new generation of analysis tools. The ultimate goal of this project is to statistically quantify how unique multi-scale phenomena generated in these filamentary systems, such as collisions, mergers, and self-gravity, determine the initial conditions for the formation of high-mass stars. This ERC-StG project will solve a current challenging dichotomy in star formation theory. In combination with low-mass studies, EMERGE will provide a major step towards a comprehensive model of star formation under one filamentary paradigm.
News
- 08/2024: Papers III (Socci et al 2024a) (link) and IV (Socci et al 2024b) (link) are accepted for publication
- 03/2024: Paper II (Bonanomi et al 2024) is online (link)
- 03/2024: First EMERGE paper (Hacar et al 2024) is out! (link)
- 05/2023: SODA II paper is accepted (link)
- 04/2023: The entire EMERGE team participates in the PP7 conference (link)
- 03/2022: The paper with our contribution to the Data Combination WG is finally out (see DC page)
- 06/2022: We participate in the ALMA observations of 30Dor (ESO photo-releaser)
- 05/2022: EMERGE participates in the LNdF outreach event with the ALMA Lego (ALMA-Lego page)
- 04/2022: Protostars & Planets VII review on filaments (Hacar et al 2022) (see PP7 page)
- 03/2022: SODA results - Massive ALMA data reduction using supercomputers (see SODA page)
02/2022: EMERGE group retreat
09/2021: ALminer online i-train (link)
- 06/2021: First Tools developed in EMERGE are ready! Use ALminer to query the ALMA Science Archive (link)
Work with us!
Join the EMERGE group
Last results
Early ALMA survey